
0
0
Overview
This policy brief captures the Indian and international policy landscape of PV module waste management to outline some immediate interventions needed in India to prepare for this issue. The recommendations are guided by a thorough review of the recycling processes and globally implemented regulatory and voluntary mechanisms to manage PV module waste.
Key Findings
- A responsible management of PV module waste and efficient recovery of different components would prevent the leaching of various toxic elements into the environment and render them available for the manufacturing industry.
- PV module recycling is a multistep process involving dismantling, delamination, and metal recovery. Some recycling techniques like chemical delamination yield undamaged solar cells, which could be reused directly or with little refurbishing. Mechanical and combustion delamination, on the contrary, yield damaged solar cells that need to be treated electrochemically or metallurgically to recover the metals.
PV module recycling is a multistep process
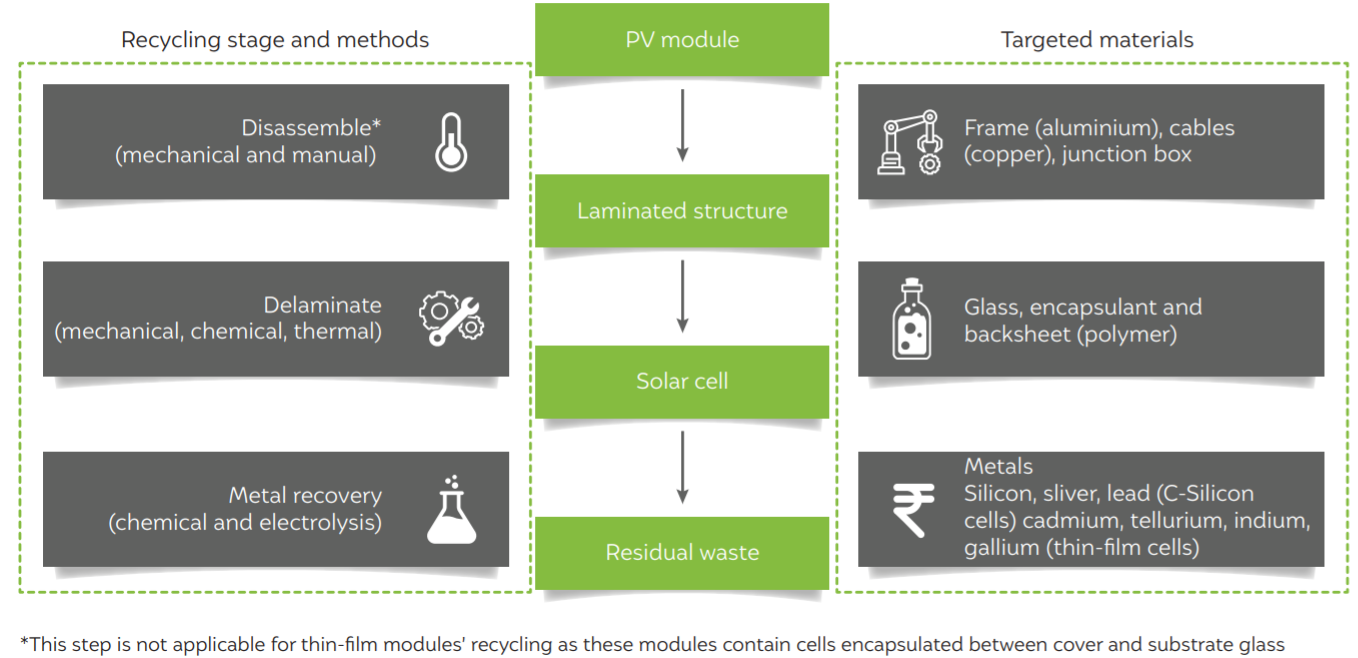
- Globally, only a few regulations cover PV modules in any waste category. The European Union (EU) is the first to revise its Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) legislation and bring PV modules under its ambit. It also provides some financing mechanisms to cover the waste management costs.
Key Recommendations
Policymakers should:
- Introduce a ban on dumping of waste modules by different entities in the landfills.
- Formulate a dedicated PV module waste management regulation.
- Introduce incentives like green certificates to provide a level-playing field and encourage recycling and mineral recovery by the industry.
Industries should:
- Improve the PV module design to minimise the waste at the disposal stage. This can include sustainable design with reduced use of toxic minerals or adopting a ‘design to disassemble’ approach.
- Invest in the second-life use of sub-standard modules to delay waste creation.
- Collaborate with research institutes to develop recycling techniques and support pilot demonstrations.
- Conceptualise new business models to manage and finance the waste disposal.















